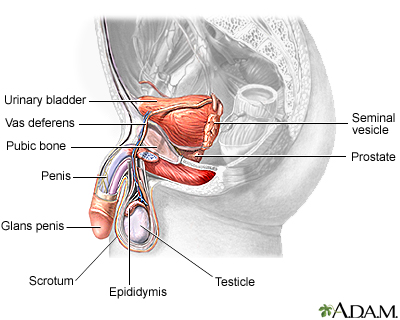
The prostate gland is a vital part of the male reproductive system. Situated just below the bladder and in front of the rectum, it is a small organ that plays a significant role in men's health. Shaped like a walnut, this gland surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the penis. It is crucial for understanding the functions and purpose of the prostate gland in maintaining overall well-being.
1. Structure and Position
The prostate gland is divided into several sections, each with its own distinct function. It is composed of glandular tissue, fibrous tissue, and smooth muscle fibers. Positioned just below the bladder, it sits right in front of the rectum. Its location allows for the gland to be examined through a rectal exam, aiding in the diagnosis of potential health concerns.
2. Production of Seminal Fluid
The primary function of the prostate gland is to produce seminal fluid. Seminal fluid, also known as semen, acts as a carrier for sperm during ejaculation. The prostate gland contributes to about 30% of the total volume of seminal fluid. The fluid produced by the prostate gland contains various enzymes, proteins, and minerals that provide nourishment and enhance the survival of sperm.
3. Regulation of Urine Flow
Due to its position around the urethra, the prostate gland plays a role in regulating urinary flow. It helps control the urine flow by contracting and relaxing the smooth muscle fibers in its tissue. However, as men age, the prostate gland may enlarge and exert pressure on the urethra, leading to various urinary problems such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, or difficulty in emptying the bladder.
4. Potential Health Concerns
Problems associated with the prostate gland can arise, primarily due to age-related changes. Common conditions include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate), and prostate cancer. Regular check-ups and early detection are crucial in managing these conditions effectively. Understanding the prostate gland and its functions can prompt timely medical intervention, improving overall prognosis and quality of life.
In conclusion, the prostate gland plays a crucial role in men's reproductive and urinary health. While it may be a small organ, it is essential in producing seminal fluid, regulating urine flow, and maintaining overall well-being. Understanding the functions and potential health concerns associated with the prostate gland empowers individuals to prioritize their health and seek appropriate medical attention when needed. Regular screenings and open communication with healthcare professionals ensure a proactive approach to men's health concerns.
Related FAQs about what is the prostate gland
What are the common health concerns associated with the prostate gland?
Common health concerns related to the prostate gland include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer.
How does the prostate gland affect urinary functions?
The prostate gland can impact urinary functions by regulating urine flow. However, an enlarged prostate can lead to urinary problems like frequent urination and weak urine flow.
What is the role of the prostate gland in male reproductive health?
The prostate gland is responsible for producing seminal fluid, which carries and nourishes sperm during ejaculation.
Where is the prostate gland located in the male body?
The prostate gland is located just below the bladder, in front of the rectum.
When should men consider seeking medical attention for prostate-related issues?
Men should seek medical attention for prostate-related concerns if they experience symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty in emptying the bladder, or any other changes in urinary or reproductive functions that cause concern.
