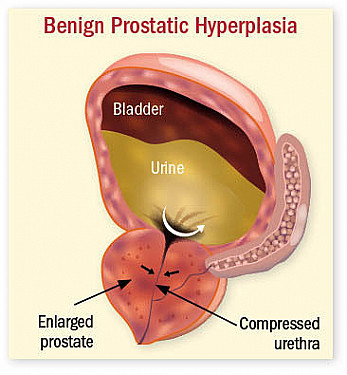
An enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition that affects many men as they age. This condition can cause bothersome urinary symptoms and impact overall quality of life. If you or a loved one is dealing with an enlarged prostate, you may be wondering what the best treatment options are available. In this blog post, we will explore various approaches to managing an enlarged prostate, focusing on medications, minimally invasive procedures, and lifestyle changes.
Medications
When it comes to treating an enlarged prostate, medications are often the first line of defense. There are two main categories of medications commonly prescribed for BPH: alpha blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. Alpha blockers work by relaxing the muscles in the prostate and bladder, making it easier to urinate. On the other hand, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors target the hormones that cause prostate enlargement. These medications can help shrink the prostate over time and improve urinary symptoms. It's important to note that medication effectiveness may vary from person to person, and some individuals may need to try different medications or combinations of medications to find the optimal treatment.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For individuals who do not experience sufficient relief from medications or prefer a non-pharmacological approach, minimally invasive procedures can be an excellent option. These procedures aim to relieve symptoms by reducing prostate tissue and improving urine flow. One commonly used procedure is called transurethral microwave therapy (TUMT). During TUMT, a microwave antenna is inserted into the urethra to deliver targeted heat to the prostate, causing the excess tissue to shrink. Another procedure, transurethral needle ablation (TUNA), involves using radiofrequency energy to heat and destroy prostate tissue. Other minimally invasive procedures include prostatic urethral lift (UroLift), which uses tiny implants to hold the enlarged prostate tissue away from the urethra, and water-induced thermotherapy (WIT), which employs heated water vapor to reduce excess prostate tissue. These procedures typically offer quicker recovery times and fewer complications compared to traditional surgery.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medication and minimally invasive procedures, certain lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms of an enlarged prostate. These changes may not cure the condition, but they can provide relief and improve overall well-being. Some beneficial lifestyle modifications include:
1. Limiting fluid intake, especially before bedtime, to reduce nighttime urination
2. Avoiding caffeine and alcohol, as they can aggravate urinary symptoms
3. Practicing pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegels, to strengthen the muscles that control urination
4. Maintaining a healthy weight, as obesity can worsen symptoms
5. Regularly emptying the bladder completely to minimize urinary retention
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on how to incorporate these lifestyle changes effectively.
Conclusion
When it comes to finding the best treatment for an enlarged prostate, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The optimal approach will depend on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, personal preferences, and overall health. Medications, minimally invasive procedures, and lifestyle changes all play a significant role in managing this condition. It's crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan. By considering all available options, individuals with an enlarged prostate can find relief and regain control over their urinary health.
Related FAQs about what is the best treatment for enlarged prostate
What medications are commonly used to treat an enlarged prostate?
Alpha blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are commonly used medications to treat an enlarged prostate. Alpha blockers relax the muscles around the prostate, improving urine flow, while 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can shrink the prostate over time.
What are the minimally invasive procedures for treating an enlarged prostate?
Some minimally invasive procedures for treating an enlarged prostate include Transurethral Microwave Therapy (TUMT), Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA), and Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL). TUMT uses microwave energy to destroy prostate tissue, TUNA utilizes radio waves to burn away excess tissue, and PUL involves placing small implants to hold the prostate lobes apart, reducing blockage.
When is surgery considered for treating an enlarged prostate?
Surgery is typically considered for treating an enlarged prostate when other treatment options have failed or in severe cases. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) and Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) are common surgical procedures used to remove excess prostate tissue and alleviate symptoms.
Is consultation with a urologist necessary before choosing a treatment?
Yes, it is important to consult with a urologist before choosing a treatment for an enlarged prostate. A urologist will evaluate your specific situation, including the size of your prostate, severity of symptoms, and overall health, to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for you.
Which treatment option is the best for me?
The best treatment for an enlarged prostate varies depending on individual circumstances. Your urologist will recommend the most suitable option based on factors such as the severity of your symptoms, prostate size, and your overall health. It is important to discuss and weigh the potential benefits and risks of each treatment option with your doctor to make an informed decision.
Glossary about what is the best treatment for enlarged prostate
1. enlarged prostate: Enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a medical condition in which the prostate gland enlarges, causing difficulties in urination.
2. treatment: Treatment refers to the medical interventions and procedures employed to alleviate or cure a specific health condition, in this case, the enlarged prostate.
3. benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, commonly found in older men. BPH can cause urinary difficulties and other symptoms.
4. prostate gland: The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system and is responsible for producing semen. It surrounds the urethra, the tube carrying urine from the bladder out through the penis.
5. urination: Urination, also known as micturition, is the process of emptying the bladder through the urethra. Difficulties in urination can occur due to an enlarged prostate.
6. medical condition: A medical condition refers to a disorder, ailment, or illness affecting the health of an individual, in this case, the enlargement of the prostate gland.
7. interventions: Interventions refer to the various medical treatments and procedures undertaken to address a specific health condition or problem.
8. procedures: In the medical context, procedures refer to the step-by-step actions or methods executed to diagnose, treat, or manage a particular health issue.
9. symptoms: Symptoms are the subjective indicators or manifestations experienced by a person suffering from a medical condition. Symptoms of an enlarged prostate may include frequent urination, weak urine flow, or difficulty starting and stopping urination.
10. reproductive system: The reproductive system is a collection of organs and tissues involved in the reproductive process. In males, it includes structures such as the prostate gland.
