Understanding Progesterone and Its Role in the Body
Progesterone, often known as the "pregnancy hormone," is a vital hormone found in both males and females. It plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and preparing the uterus for pregnancy. Produced in the ovaries, adrenal glands, and placenta during pregnancy, progesterone levels fluctuate throughout a woman's monthly cycle.
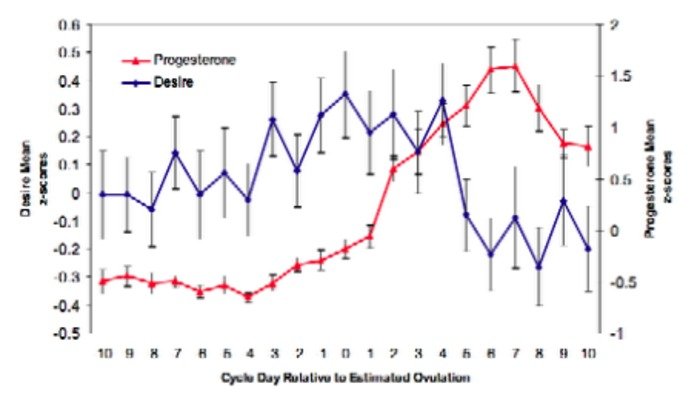
The Connection Between Progesterone and Sex Drive
While progesterone is essential for ensuring reproductive functions, its direct impact on sex drive is still a subject of debate among experts. Some studies suggest that progesterone may boost libido due to its ability to promote relaxation and enhance mood. However, other research indicates that progesterone might have a minimal effect on sexual desire, and various other factors play more significant roles in determining one's sex drive.
Progesterone and Menopause
During menopause, a woman's progesterone levels naturally decline. This hormonal shift can lead to symptoms like vaginal dryness and decreased libido. Although hormonal replacement therapies are available to alleviate these symptoms, the effect of progesterone on sex drive remains inconclusive. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before considering any hormone-based treatments.
The Influence of Other Factors on Sexual Desire
Sexual desire is a complex interplay of many factors, and while progesterone may have some impact, it is overshadowed by other determinants. Stress, relationship dynamics, physical health, lifestyle habits, and psychological well-being are all crucial influencers of libido. Neglecting these factors while solely relying on progesterone may not produce the desired results.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If you are experiencing a decrease in sex drive or have concerns about your hormonal levels, consulting a healthcare provider is essential. A medical professional can help determine the underlying causes and develop a personalized treatment plan to address your specific needs. They may suggest hormone therapy or recommend lifestyle changes to improve overall well-being.
Conclusion
While some believe that progesterone may increase sex drive, the evidence supporting this claim is inconclusive. Progesterone plays a vital role in reproductive health but may have a minimal direct impact on libido. Understanding the multifaceted nature of sexual desire and considering various factors beyond hormone levels is crucial when seeking ways to enhance libido. Remember, professional guidance is indispensable for interpreting your body's unique needs and charting the most appropriate path forward.
By prioritizing holistic well-being and addressing the various factors that influence your sex drive, you can work towards improving your overall sexual health and satisfaction.Related FAQs about does progesterone increase sex drive
What is the role of progesterone in the body?
Progesterone plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and preparing the uterus for pregnancy. It is also involved in maintaining pregnancy and is produced in the ovaries, adrenal glands, and placenta.
Does progesterone increase sex drive?
The impact of progesterone on sex drive is still debated among experts. While some studies suggest it may have a positive effect due to relaxation and mood enhancement, other research indicates that progesterone may have minimal direct influence on sexual desire.
Does progesterone affect libido during menopause?
During menopause, progesterone levels naturally decline. This hormonal shift can contribute to symptoms like vaginal dryness and decreased libido. While hormone replacement therapies are available to alleviate some symptoms, the effect of progesterone on sex drive during this stage remains inconclusive.
What other factors influence sexual desire apart from progesterone?
Many factors contribute to sexual desire, such as stress, relationship dynamics, physical health, lifestyle habits, and psychological well-being. These factors often play more significant roles in determining libido than progesterone levels alone.
When should I seek professional guidance regarding progesterone and sex drive?
If you are experiencing a decrease in sex drive or have concerns about your hormonal levels, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider. They can help determine the underlying causes and develop a personalized treatment plan based on your specific needs.
Glossary about does progesterone increase sex drive
1. Progesterone: Progesterone is a hormone found in both males and females that plays a vital role in regulating the menstrual cycle and preparing the uterus for pregnancy. It is produced in the ovaries, adrenal glands, and placenta during pregnancy.
2. Libido: Libido refers to a person's overall sexual desire or drive. It is influenced by a variety of factors such as hormones, psychological well-being, stress levels, physical health, and relationship dynamics.
3. Menopause: Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman's reproductive years. It usually occurs in the late 40s or early 50s and is characterized by the cessation of menstruation and a decline in hormone levels, including progesterone.
4. Hormonal Replacement Therapies: Hormonal replacement therapies are treatments that aim to alleviate the symptoms of menopause by supplementing or replacing hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone. These therapies are prescribed under medical supervision.
5. Stress: Stress refers to the body's response to demanding situations or life events. High levels of stress can negatively impact libido and overall sexual desire. Managing stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy sex drive.
6. Relationship Dynamics: Relationship dynamics refer to the interactions and patterns of behavior between individuals in a relationship. Healthy communication, emotional intimacy, and mutual satisfaction can positively influence sexual desire.
7. Physical Health: Physical health refers to the overall well-being and condition of an individual's body. Factors such as exercise, nutrition, and chronic health conditions can impact libido and sexual function.
8. Lifestyle Habits: Lifestyle habits encompass behaviors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of sleep, and poor diet. Unhealthy lifestyle choices can contribute to a decrease in sex drive and overall sexual health.
9. Psychological Well-being: Psychological well-being refers to an individual's emotional and mental state. Factors like stress, anxiety, depression, self-esteem, and body image can all influence sexual desire and satisfaction.
10. Holistic Well-being: Holistic well-being refers to the overall balance and harmony of an individual's physical, emotional, mental, and social health. Focusing on all aspects of well-being is essential for a fulfilling sex life.
