Debunking the Weight Loss and Penis Size Myth
One common misconception that often circulates among men is the belief that losing weight can increase the size of their penis. However, the reality is quite different. Let's dive deeper into the subject and explore whether there is any truth to this belief.
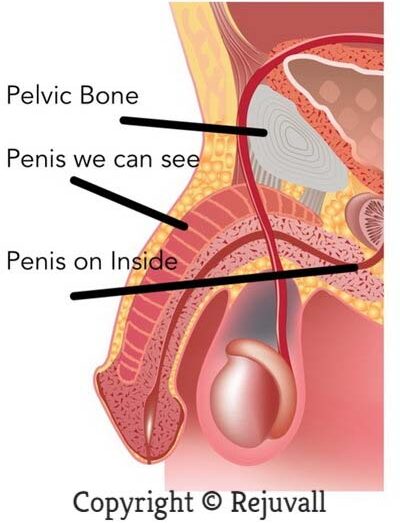
Understanding the Factors Influencing Penis Size
Firstly, it is important to understand that penis size is primarily determined by genetics and hormones rather than weight. During puberty, the penis undergoes growth due to hormonal changes, contributing to its final size. This means that regardless of weight, genetics largely dictate how big or small your penis will be.
The Impact of Weight Loss on Penis Appearance
While losing weight may not directly increase the size of your penis, it can have an impact on its appearance. Excess weight can lead to the accumulation of fat cells in the pelvic region and around the base of the penis. Losing weight can help reduce this surrounding fat, potentially making the penis appear larger as it is no longer hidden by excess fatty tissues.
However, it is crucial to note that this perceived increase in size is merely due to the elimination of excess fat, rather than actual physiological changes in the penis itself.
Other Benefits of Weight Loss on Sexual Health
Weight loss offers numerous benefits to overall sexual health, positively impacting various aspects beyond penis size. Shedding those extra pounds can enhance blood circulation throughout the body, including the genital area, which may result in better erectile function and overall sexual performance. Additionally, weight loss can boost self-confidence and body image, leading to improved sexual experiences with your partner.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, losing weight alone is unlikely to increase the size of your penis. Genetics and hormones primarily determine penis size, and weight loss does not alter this fundamental aspect. However, shedding pounds can positively impact the appearance of the penis by reducing surrounding fat, creating the illusion of a larger size. More importantly, weight loss brings about a range of benefits to overall sexual health, including improved blood circulation and enhanced self-confidence. So while you might not experience a physical transformation down there through weight loss, your sexual well-being can certainly benefit from maintaining a healthy weight.
Related FAQs about does losing weight increase penis size
Does losing weight increase penis size?
No, losing weight does not directly increase penis size. Penis size is primarily determined by genetics and hormones, rather than weight loss.
Can losing weight make the penis appear larger?
Losing weight can potentially make the penis appear larger by reducing surrounding fat. However, this is merely an optical illusion caused by the elimination of excess fatty tissues, rather than actual physiological changes in penis size.
What factors influence penis size?
Penis size is mainly influenced by genetics and hormonal changes during puberty. Weight loss does not alter these factors.
Are there any benefits of weight loss on sexual health?
Yes, weight loss can bring various benefits to sexual health. It can improve blood circulation, leading to better erectile function, and enhance overall sexual performance. Additionally, weight loss can boost self-confidence and body image, positively impacting sexual experiences.
Is there anything else one can do to positively impact penis size?
Apart from genetics and hormonal factors, there is no proven method to permanently increase penis size. Various exercises, devices, or supplements claiming to increase penis size have not been scientifically proven to have a significant effect.
Glossary about does losing weight increase penis size
1. Genetics: Genetics refers to the study of genes and heredity, specifically how traits and characteristics are passed down from one generation to another.
2. Hormones: Hormones are chemical substances produced by the endocrine glands, which regulate various bodily functions and processes, including growth, development, metabolism, and reproduction.
3. Puberty: Puberty is the stage of development during which adolescents undergo physical and physiological changes, leading to sexual maturation, the ability to reproduce, and other secondary sexual characteristics.
4. Blood circulation: Blood circulation refers to the movement of blood throughout the body, facilitated by the pumping action of the heart. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to cells, while removing waste products.
5. Erectile function: Erectile function pertains to the ability to achieve and maintain an erection, which is necessary for sexual intercourse. It involves the interaction between the nervous system, blood vessels, muscles, and hormones.
6. Self-confidence: Self-confidence is a belief in one's own abilities, worth, and self-worth. It is a subjective perception that can positively or negatively influence various aspects of life, including relationships and sexual experiences.
7. Body image: Body image refers to an individual's perception, thoughts, and feelings about their own body and physical appearance. It can impact self-esteem and overall well-being, including sexual confidence and satisfaction.
8. Sexual well-being: Sexual well-being encompasses the physical, emotional, mental, and social aspects of sexual health. It involves having pleasurable and satisfying sexual experiences, as well as maintaining healthy relationships.
