Proteins: The Building Blocks of Life
Proteins are the fundamental building blocks of life that play a vital role in countless biological processes. From structurally supporting cells to catalyzing biochemical reactions, proteins are crucial for our existence. But what about sperms? Do they also contain proteins?
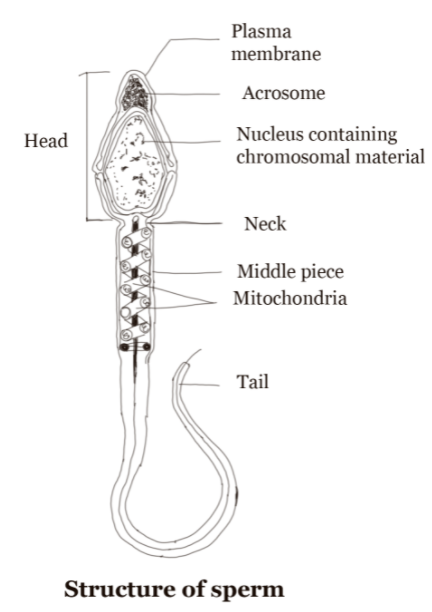
The Truth Behind Sperms and Proteins
Contrary to popular belief, sperms indeed contain proteins. In fact, proteins make up a significant portion of the composition of a sperm. These tiny, flagellated cells that set out on their remarkable journey towards fertilization are equipped with a diverse array of proteins that are crucial for their functions.
Proteins in sperms have various roles, ranging from providing structural support and motility to protecting and enabling the fertilization process. Let's delve deeper into the significance of proteins in sperms.
The Significance of Proteins in Sperms
One of the key roles of proteins in sperms is providing them with the necessary motility to reach the egg. Flagellar proteins form the core of the sperm's tail, enabling it to swim through the complex female reproductive tract towards its destination.
Furthermore, proteins called chaperones are involved in the proper folding of proteins within sperms. These chaperones ensure that the proteins maintain their functional structures, allowing the sperm to perform vital functions effectively.
Proteins also play a crucial role in protecting sperms from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can damage sperm cells, potentially leading to reduced fertility or even infertility. Antioxidant proteins safeguard the integrity of sperms and help maintain their viability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sperms do contain proteins, and these proteins are of paramount importance for their proper functioning. From providing motility to protecting against oxidative stress, proteins play crucial roles in the remarkable journey of sperms towards fertilization. Understanding the significance of proteins in sperms allows us to appreciate the intricate mechanisms that drive the miracle of life.
So, the next time you ponder whether sperms have proteins, remember that they are not just tiny cells with a singular mission, but complex entities comprised of proteins that ensure their successful voyage in the pursuit of life.
References:
- Smith, N. D., Cherr, G. N., & Mukai, C. (2013). Proteomic characterization of sperm proteins. Proteomics in human reproduction, 318-331.
- Mahfuz, I., & Hossain, M. M. (2020). Proteins associated with sperm maturation, epididymal spermiation and ejaculation. International Journal of Veterinary Science and Medicine, 8(1), 1-8.
Related FAQs about do sperms have proteins
Do sperms contain proteins?
Yes, sperms do contain proteins. Proteins make up a significant portion of the composition of a sperm.
What is the significance of proteins in sperms?
Proteins in sperms have various roles, including providing motility, protecting against oxidative stress, and enabling the fertilization process.
How do proteins contribute to sperm motility?
Flagellar proteins in sperms form the core of the tail, allowing them to swim through the female reproductive tract towards the egg.
Do proteins in sperms play a role in fertilization?
Yes, proteins in sperms contribute to the process of fertilization by enabling the sperm to bind to and penetrate the egg.
Are there proteins that protect sperms from damage?
Antioxidant proteins in sperms play a crucial role in protecting them from oxidative stress, which can damage sperm cells and potentially affect fertility.
Glossary about do sperms have proteins
1. Proteins: Proteins are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. They play a vital role in various biological processes, including structural support, catalyzing biochemical reactions, and carrying out cellular functions.
2. Sperms: Sperms, also known as spermatozoa, are the male reproductive cells or gametes of an organism. These small, motile cells are crucial for sexual reproduction as they are responsible for fertilizing the egg.
3. Flagellated: Flagellated refers to the presence of a whip-like appendage called a flagellum, which allows cells (such as sperms) to move and swim through fluid environments. In sperms, the flagellum is responsible for providing motility.
4. Motility: Motility is the ability of an organism or cell to move spontaneously and actively. In the context of sperms, motility refers to their ability to swim through the female reproductive tract towards the egg for fertilization.
5. Chaperones: Chaperones are a type of protein that assist in the proper folding of other proteins, ensuring that they acquire their functional structure. In sperms, chaperones play a role in maintaining the structural integrity of various proteins within the cells.
6. Oxidative Stress: Oxidative stress is an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the ability of cells to detoxify them or repair the resulting damage. In sperms, oxidative stress can cause damage to cells and impair their function, potentially leading to reduced fertility.
7. Antioxidant: Antioxidants are substances that can inhibit or neutralize the damaging effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In sperms, antioxidant proteins act as defense mechanisms against oxidative stress by protecting the cells from potential damage.
8. Fertilization: Fertilization is the process by which a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell, resulting in the formation of a zygote. This union of genetic material from both parents initiates the development of a new individual.
9. Infertility: Infertility refers to the inability to conceive or carry a pregnancy to full term. In the context of sperms, infertility can result from various factors, including abnormalities in sperm production, motility, or function.
10. Miracle of Life: Miracle of Life refers to the wondrous and awe-inspiring process of reproduction, which involves the creation of new life. It encompasses the complexities and intricate mechanisms through which fertilization occurs, leading to the development of a new organism.
