What is a Penile Fracture?
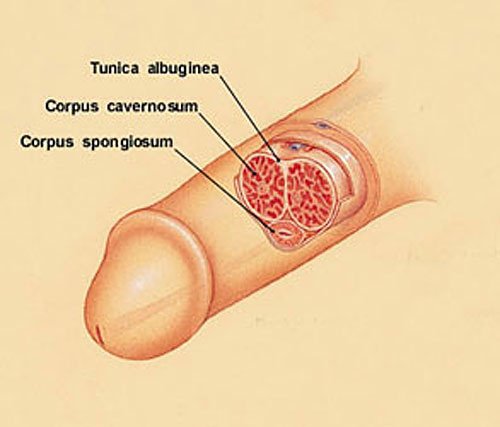
A penile fracture is a relatively rare but serious injury that can occur during sexual intercourse or other activities that put stress on the erect penis. While the term "break" may sound alarming, it refers to the rupture of the tunica albuginea, a thin and fibrous membrane that surrounds the erectile tissues.
Causes and Symptoms
Penile fractures are most commonly caused by vigorous thrusting or sudden bending of the penis during sexual activity, especially when the penis slips out and forcibly impacts the partner's body or a hard surface. The primary symptom is a cracking or popping sound, typically followed by immediate pain, swelling, bruising, and the loss of an erection.
Seeking Immediate Medical Attention
If you experience a penile fracture, it's crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Delaying treatment can lead to severe complications such as erectile dysfunction, deformities, or painful curvatures during erection. Upon examination, a medical professional may conduct physical exams or order imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or MRI, to diagnose the fracture accurately.
Treating Penile Fractures
Prompt medical treatment is vital in repairing a penile fracture and preventing long-term complications. In most cases, surgery is required to realign and repair the injury, sometimes involving the use of a graft or suturing techniques. Following surgery, a period of rest and abstinence from sexual activity is necessary for proper healing, typically lasting six to eight weeks.
Potential Long-Term Effects
While most penile fractures can be successfully treated with surgery, some individuals may experience long-term consequences. Scar tissue formation, known as Peyronie's disease, can cause painful erections, penile curvature, or difficulty with intercourse. Psychological effects such as anxiety or depression may also arise due to the trauma associated with the injury.
Prevention is Key
To minimize the risk of a penile fracture, communicate openly with your sexual partner about comfort levels and be mindful of positioning during sexual activity. Engaging in adequate foreplay and using lubrication can help reduce the chances of sudden bending or slipping out. However, accidents can still happen, so it's crucial to prioritize safe and consensual sexual practices.
Conclusion
While penile fractures are relatively rare, it's important to understand the potential risks and consequences associated with this injury. Seeking immediate medical attention, undergoing proper treatment, and allowing enough time for healing are crucial in minimizing long-term complications. Remember, maintaining open communication with your partner and prioritizing safe sexual practices can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing a penile fracture.
Related FAQs about can you break your penis
Can you break your penis?
Yes, it is possible to break your penis. Penile fractures occur when the tunica albuginea, a fibrous membrane surrounding the erectile tissues, ruptures.
What causes a penile fracture?
A penile fracture is typically caused by vigorous thrusting or sudden bending of the erect penis during sexual activity. It can occur when the penis slips out and forcefully hits the partner's body or a hard surface.
What are the symptoms of a penile fracture?
Common symptoms of a penile fracture include a cracking or popping sound, immediate pain, swelling, bruising, and the loss of an erection.
What should I do if I think I've had a penile fracture?
If you suspect a penile fracture, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Delaying treatment can lead to complications such as erectile dysfunction or painful curvatures during erection.
How are penile fractures treated?
Surgery is typically required to repair a penile fracture. The procedure aims to realign and mend the ruptured tissues, often using a graft or suturing techniques. Following surgery, a period of rest and abstinence from sexual activity is necessary for proper healing.
Glossary about can you break your penis
1. Penile Fracture: A penile fracture refers to the rupture of the tunica albuginea, a thin and fibrous membrane surrounding the erectile tissues, resulting from vigorous thrusting or sudden bending of the erect penis.
2. Tunica Albuginea: The tunica albuginea is a fibrous membrane that surrounds the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum, the erectile tissues of the penis.
3. Erectile Tissues: The erectile tissues of the penis include the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum, which fill with blood during an erection, causing the penis to become firm.
4. Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging, also known as sonography, uses sound waves to create images of the body's internal structures and can be employed to diagnose a penile fracture.
5. MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body's internal structures.
6. Peyronie's Disease: Peyronie's disease is a condition characterized by the formation of scar tissue in the penis, resulting in painful erections, penile curvature, or difficulty with sexual intercourse.
7. Scar Tissue: Scar tissue is fibrous connective tissue that replaces normal tissue when it is damaged or injured, often leading to abnormal function or structure in the affected area.
8. Safe Sexual Practices: Safe sexual practices refer to behaviors and precautions taken to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections, unwanted pregnancies, or injuries during sexual activity.
